SpaceX Lunar Starship (Human Landing System):
Blue Origin Blue Moon MK2 lander:
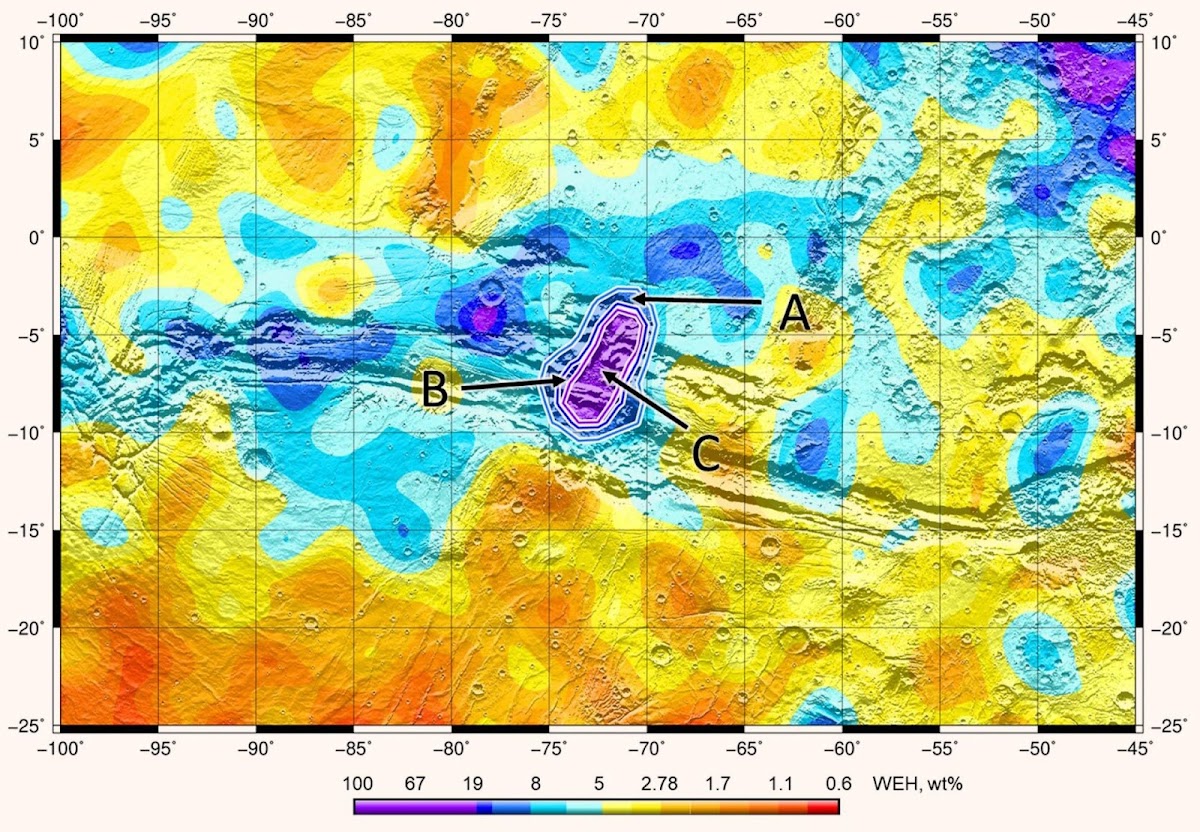
Map of Artemis III candidate Landing sites:
 On May 29th at Starbase, Texas SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided an update of SpaceX's Starship Mars architecture "The Road to Making Life Multiplanetary". Here are slides from his presentation.
On May 29th at Starbase, Texas SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided an update of SpaceX's Starship Mars architecture "The Road to Making Life Multiplanetary". Here are slides from his presentation.
 On April 4th at Starbase, Texas SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided an unannounced update of SpaceX's Starship architecture. Here are slides and animations from his presentation.
On April 4th at Starbase, Texas SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided an unannounced update of SpaceX's Starship architecture. Here are slides and animations from his presentation.
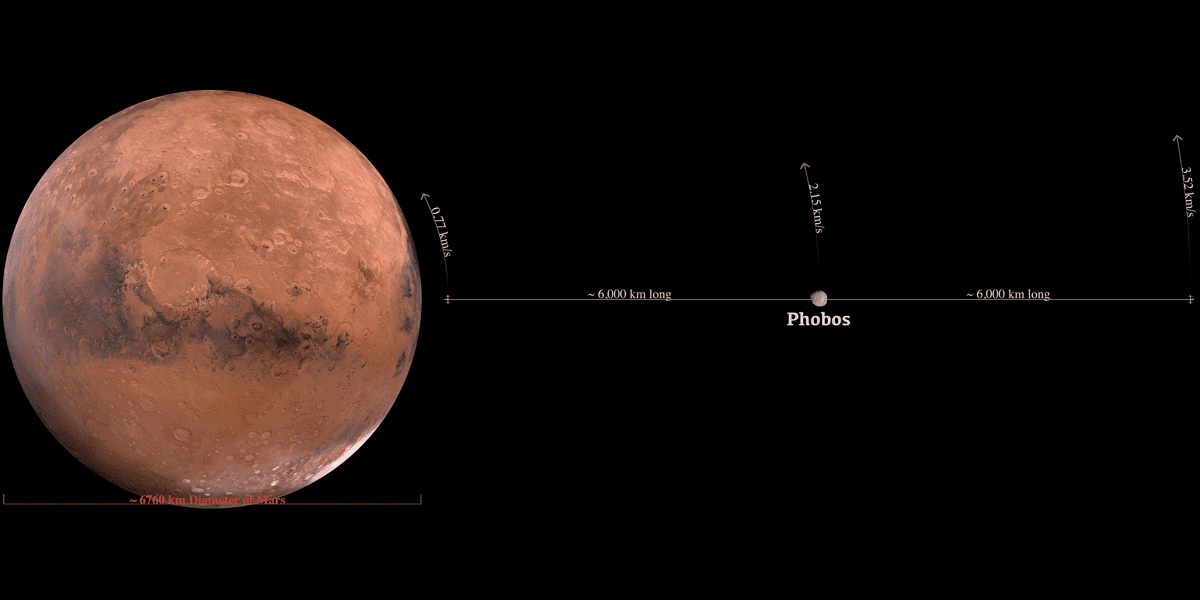 Building a Martian space elevator would be complicated by the Martian moon Phobos, which is in a low orbit at ~6,028 km above the Martian surface and intersects the Equator regularly, thus getting in the way of a traditional geostationary space elevator. But there is an idea instead to build a space elevator from Phobos itself.
Building a Martian space elevator would be complicated by the Martian moon Phobos, which is in a low orbit at ~6,028 km above the Martian surface and intersects the Equator regularly, thus getting in the way of a traditional geostationary space elevator. But there is an idea instead to build a space elevator from Phobos itself.
 On February 10th SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided the latest update of SpaceX's Starship architecture. Here are slides and animations from his presentation.
On February 10th SpaceX CEO and lead designer Elon Musk provided the latest update of SpaceX's Starship architecture. Here are slides and animations from his presentation.